What Really Causes Eczema? Understanding the Root Problem
Aug 15, 2025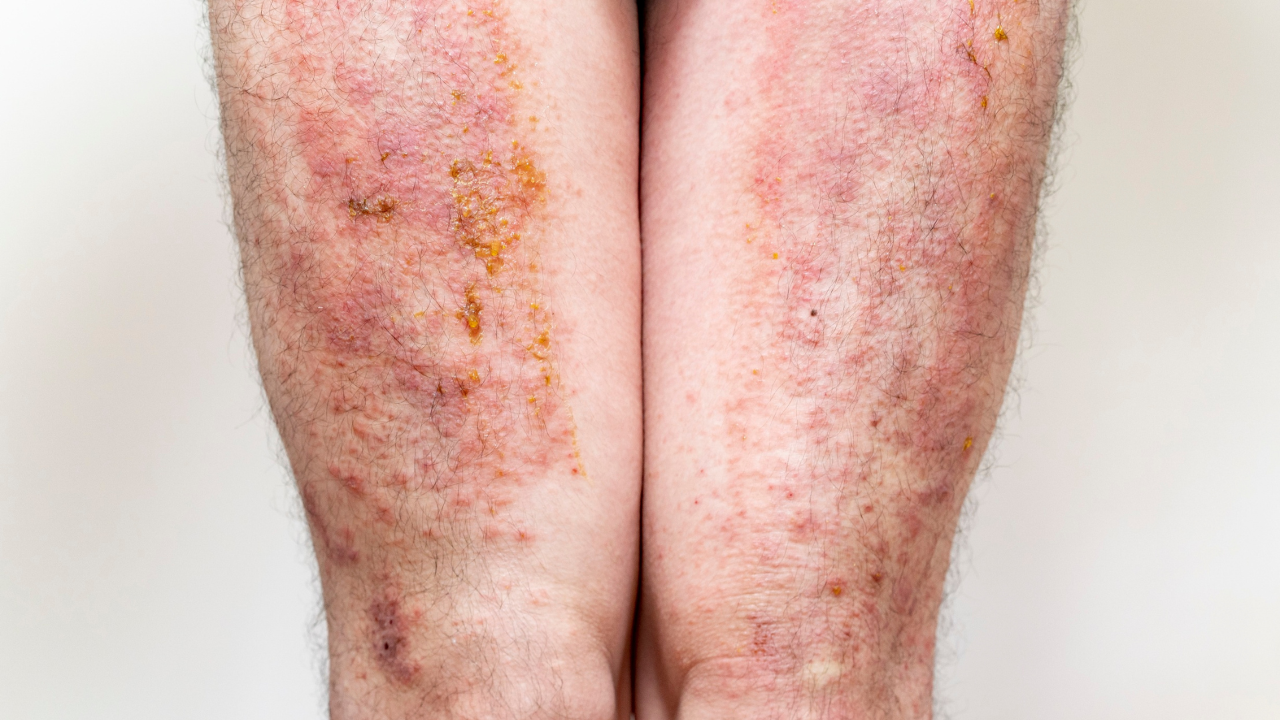
If you have eczema (also known as atopic dermatitis), you’ve probably wondered:
✔ Why does my skin flare up?
✔ Why does it feel so itchy and dry all the time?
✔ Is it just allergies or something deeper?
The truth is, eczema is not just a skin problem. It’s an immune system issue combined with a weak skin barrier, and many factors—from genetics to diet—play a role. Let’s break it down step by step.

1. Your Skin Barrier Is Broken
Think of your skin as a brick wall:
- Bricks = skin cells
- Cement = lipids like ceramides
In eczema, the “cement” is weak. Here’s why:
- Filaggrin mutation: Many people with eczema have a gene mutation in filaggrin, a protein that keeps skin strong and hydrated.
- Low ceramides and moisture: Eczema-prone skin has fewer natural oils and moisturizing factors, leading to dryness and cracks.
- These cracks allow:
✔ Allergens
✔ Irritants
✔ Bacteria
to get inside and cause inflammation.
2. Your Immune System Overreacts
When your skin barrier is weak, your immune system goes into overdrive.
- Acute flare-ups = Th2 immune response dominates
✔ Key players: IL-4, IL-13, IL-5 (inflammatory messengers)
✔ They reduce filaggrin even more → weaker barrier
✔ Increase IgE (allergy antibodies) → more sensitivity
✔ Recruit eosinophils → more inflammation - Chronic eczema = more immune cells join the fight
✔ Th1 and Th17 cells release cytokines like IFN-γ and IL-17
✔ Skin becomes thicker and rougher (lichenification)
3. Bacteria Make Things Worse
Did you know 90% of eczema patches contain Staphylococcus aureus bacteria?
- This bacteria releases toxins called superantigens → they make your immune system even more inflamed.
- Normally, friendly bacteria like Staphylococcus epidermidis help balance things out, but in eczema, you lose this protection.
4. The Itch-Scratch Cycle Is Real
Ever feel like you just can’t stop scratching? That’s because of IL-31, an itch-causing molecule that activates nerve cells.
- Scratching causes more skin damage → more inflammation → more itch.
- It becomes a vicious cycle.
5. How Does Diet Affect Eczema?
Food isn’t the main cause of eczema, but it can make inflammation worse.
- Too much sugar: Spikes insulin and increases inflammatory chemicals like IL-6 and TNF-α.
- Processed foods: Contain additives and unhealthy fats that cause inflammation and disrupt gut bacteria.
- Gut-skin connection: An unhealthy gut microbiome can trigger immune reactions that show up on your skin.
6. Environmental Triggers Make It Worse
Common triggers include:
✔ Allergens: Dust mites, pollen, pet dander, mold
✔ Harsh products: Fragrances, sulfates, parabens in soaps and skincare
✔ Weather changes: Dry air, cold, heat
What you can do:
- Use fragrance-free, hypoallergenic skincare
- Keep your home clean and dust-free
- Wear protective clothing in harsh weather
Key Takeaways
- Eczema is not just dry skin; it’s an immune and skin barrier problem.
- Genes, immune imbalance, bacteria, diet, and environment all play a role.
- Lifestyle changes (clean diet, allergen control, proper skincare) help prevent flare-ups.
Need Help Calming Your Eczema?
Download our Soothe Skin Secret eBook
Get Your Guide Here
GET THIS FOR FREE!
The Ultimate Anti-Inflammatory Recipe Guide: Clear Your Skin & Boost Your Health Naturally
We hate SPAM. We will never sell your information, for any reason.

